Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO)
Gut microbes live symbiotically within the human digestive tract and play important roles in host defense, immunity, and nutrient processing and absorption. This diverse community is unique to each person and influenced by acute and chronic dietary exposures to various food sources.
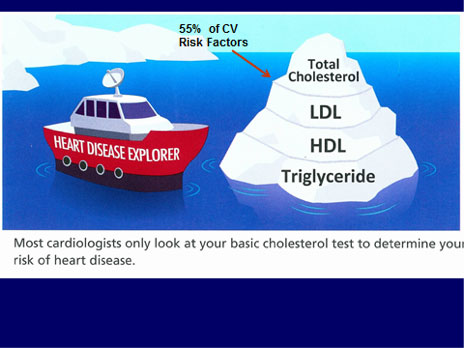
Nutrients such as phosphatidylcholine (also known as lecithin), choline, and L-carnitine are abundant in animal-derived products such as red meat, egg yolk, and full-fat dairy products. When consumed, these nutrients are processed by gut bacteria, resulting in the release of various metabolites, including TMA (trimethylamine), into the blood. TMA is then transported to the liver, where it is converted into TMAO (trimethylamine N-oxide), which has been shown to regulate various physiological processes involved in the development of atherosclerosis.i
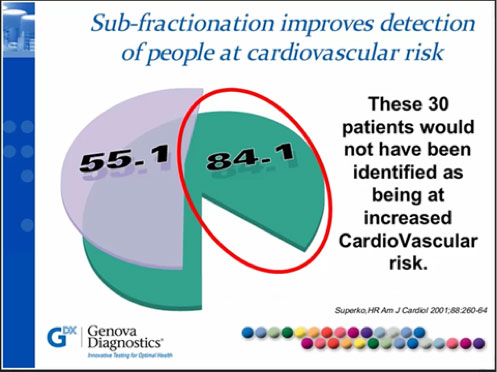
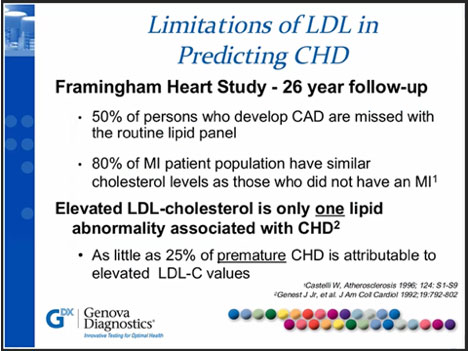
Clinical Significance: There is a dose-response relationship between TMAO and atherosclerotic burden in individuals undergoing elective diagnostic coronary angiography. In stable individuals undergoing elective cardiac evaluation, elevated TMAO levels are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, or major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE: MI, stroke or death) at a 3-year follow-up.
Plasma L-Carnitine (a dietary precursor to TMAO) is also associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease and MACE, but only in individuals with simultaneously elevated TMAO levels. In a “low risk” subset of the aforementioned population, people with optimal LDL-C 70mg/dL or apoB <80mg/dL), but elevated TMAO, were just as likely to experience a major adverse cardiovascular event.
Lab Values ((μM)
<6.2 Low
6.2-9.9 Moderate
≥10.0 High
The following are suggestions from Mark Houston, M.D., from his article, “The Role of Nutraceutical Supplements in the Treatment of Dyslipidemia.”12 Also see Figure 16.
Inhibition of LDL oxidation
Niacin
Green tea extract and green tea
Pantethine
Monounsaturated fats
Curumin
Pomegranate
Garlic
Sesame
Gamma ⁄ delta tocotrienols
Lycopene
Polyphenols
Oleic acid
Glutathione
Citrus bergamot
Policosanol
Inhibition of low-density lipoprotein glycation
Carnosine
Histidine
Myricetin
Kaempferol
Rutin
Morin
Pomegranate
Organosulfur compounds
Lower low-density lipoprotein
Niacin
Red yeast rice
Plant sterols
Sesame
Tocotrienols (gamma ⁄ delta)
Pantethine
Citrus bergamot
Green tea extract and green tea
Omega 3 fatty acids
Flax seed
Monounsaturated fats
Garlic
Resveratrol
Curcumin
Orange juice
Soluble fiber
Krill oil
Convert dense low-density lipoprotein B to large low-density lipoprotein A
Niacin
Omega 3 fatty acids
Plant sterols
Reduce intestinal cholesterol absorption
Plant sterols
Soy
Green tea extract and green tea
Flax seeds
Sesame
Garlic
Fiber
HMG CoA reductase inhibition (decrease cholesterol production)
Red yeast rice
Pantethine
Gamma ⁄ tocotrienols
Sesame
Green tea extract and green tea
Omega 3 fatty acids
Citrus bergamot
Garlic
Curcumin
Gamma-linolenic acid
Plant sterols
Lower lipoprotein(a)
Niacin
N acetyl cysteine
Gamma delta tocotrienols
Omega 3 fatty acids
Flax seed
Coenzyme Q10
Vitamin C
L Carnitine
L-Lysine
L-Arginine
Lower triglycerides
Niacin
Red yeast rice
Omega 3 fatty acids
Pantethine
Citrus bergamot
Flax seed
Monounsaturated fats
Resveratrol
Orange juice
Krill oil
Increase total high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and HDL 2b levels and convert HDL 3 to HDL 2 and 2b
Niacin
Omega 3 fatty acids
Pantethine
Red yeast rice
Monounsaturated fats
Resveratrol
Curcumin
Pomegranate
Orange juice
Citrus bergamot
Krill oil
Reduce inflammation
Niacin
Omega 3 fatty acids
Flax seed
Monounsaturated fats
Plant sterols
Guggulipids
Resveratrol
Glutathione
Lower apolipoprotein B lipoprotein
Increase apolipoprotein A1 lipoprotein
Decrease low-density lipoprotein particle number
Lower apolipoprotein B lipoprotein
Niacin
Omega 3 fatty acids
Plant sterols
Green tea extract and green tea
Increase apolipoprotein A1 lipoprotein
Niacin
Decrease low-density lipoprotein particle number
Niacin
Omega 3 fatty acids
Nutraceutical Supplement Recommended Doses For The Treatment Of Dyslipidemia
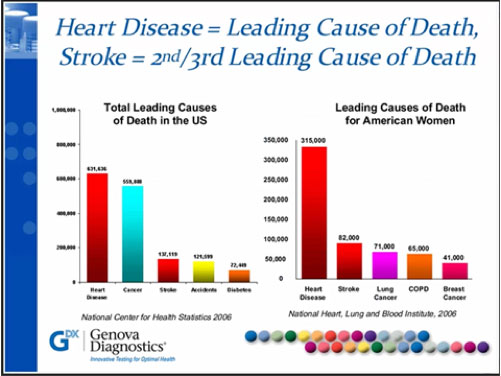
 About 610,000 people die of heart disease in the U.S. every year — 1 in every 4 deaths.[1]
About 610,000 people die of heart disease in the U.S. every year — 1 in every 4 deaths.[1]