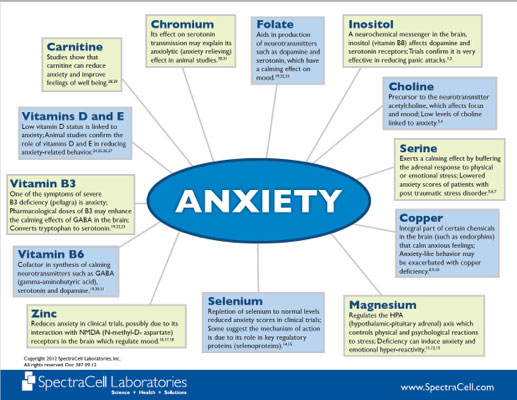
Choline: Precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which affects focus and mood, low levels of choline have been linked to anxiety.[12]
Serine: Exerts a calming effect by buffering the adrenal response to physical or emotional stress. Lowered anxiety scores of patients with post-traumatic stress disorder.[13]
Copper: An integral part of certain chemicals in the brain (such as endorphins) that calm anxious feelings, copper deficiency may exacerbate anxiety-like behavior.[14]
Magnesium: Regulates the HPA (hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal) axis, which controls physical and psychological reactions to stress; deficiency can induce anxiety and emotional hyper-reactivity.[15]
Selenium: Repletion of selenium to normal levels reduced anxiety scores in clinical trials; some suggest the mechanism of action is due to its role in key regulatory proteins (selenoproteins).[16]
Zinc: Reduces anxiety in clinical trials, possibly due to its interaction with NMDA (N-methyl-D- aspartate) receptors in the brain, which regulate mood.[17]
Vitamin B6: Cofactor in synthesis of calming neurotransmitters such as GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), serotonin and dopamine.[18]
Vitamin B3: One of the symptoms of severe B3 deficiency (pellagra) is anxiety. Pharmacological doses of B3 may enhance the calming effects of GABA in the brain, as it converts tryptophan to serotonin.[19]
Vitamins D and E: Low vitamin D status is linked to anxiety; animal studies confirm the role of vitamins D and E in reducing anxiety-related behavior.[20]
An evaluation of someone complaining of anxiety should include an extensive past medical and surgical history, medication history, family history, and history of any past traumatic events.
Bloodwork should include a CBC, CMP, complete thyroid profile with TSH, Free T4, Free T3, reverse T3, ferritin, TPO and Thyroglobulin antibodies. Other tests include fasting insulin; Hgb A1c; salivary hormone testing; food allergy panel; neurotransmitter testing; stool test if indicated to evaluate for abnormal bacteria, yeast, parasites, absorption and digestion; micronutrient analysis through SpectraCell, and neurotransmitter test through Sanesco. (See link for advanced testing-Put in Doug’s website)
Therapy
The type of therapy will depend on the results of the individual testing.
Possible therapies: Correcting metabolic dysfunctions (thyroid, insulin), balancing hormones, replacing deficient micronutrients and minerals, repairing abnormal bowel findings, and returning neurotransmitters to balance.
Psychotherapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Self-Help or Support Groups
Stress-Management Techniques
Medication
Anti-Anxiety Medications